
 Tree planting
Tree planting



 Tree planting
Tree planting


We began planting trees in 2009.
Thanks to your support, we were able to
plant approximately 1,000 seedlings.
The seedlings are still small, but we hope that a rich and green forest will spread out in 50 to 100 years to enrich the future of our planet.






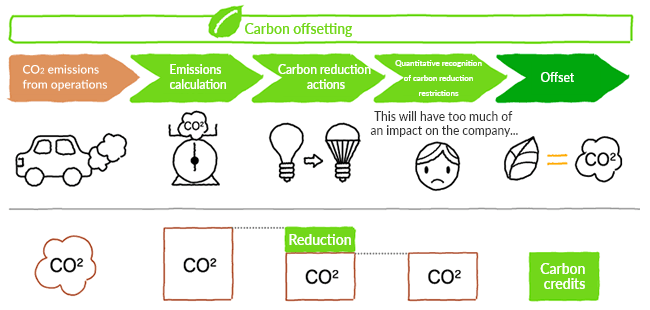
Carbon offsetting is a means of compensating for CO2 emissions that cannot be reduced by CO2 absorption and emission reduction projects like tree planting.
Carbon offsetting through tree planting promotes voluntary CO2 reduction by a wide range of entities such as companies and local citizens. At the same time, tree planting projects have also been connected with addressing poverty in the areas where trees are planted.
China's Inner Mongolia is one of the areas most susceptible to desertification, a serious problem in Inner Mongolia.
For example, China has 1.73 million square kilometers of desertified land, and China's National Forestry and Grassland Administration reported that an area of 530,000 square kilometers awaiting maintenance will take about 300 years at the current rate to restore back to health.* "People's Daily" March 15, 2011
There are various causes of desertification. There are many human factors such as logging, pasturing and excess farmland conversion, as well as problems caused by climate change as a result of human economic activities, etc. The causes are numerous and are intertwined with each other in a complex way.
Larch is a species of tree that spreads across the subarctic regions of the northern hemisphere, e.g., in Europe, Siberia, the Himalayas, North America, and Japan. It is characterized by rapid growth and resistance to dryness. (The larch absorbs about 250 kg of CO2 over a 30 year period.)
Larch trees were used in the post-war expansion of forests in Japan due to their rapid growth and easy planting. Larch trees are one of the most suitable plants for living in areas that are often impacted by severe droughts.